Why Patients Experience Hair Shedding After a Hair Transplant
Introduction
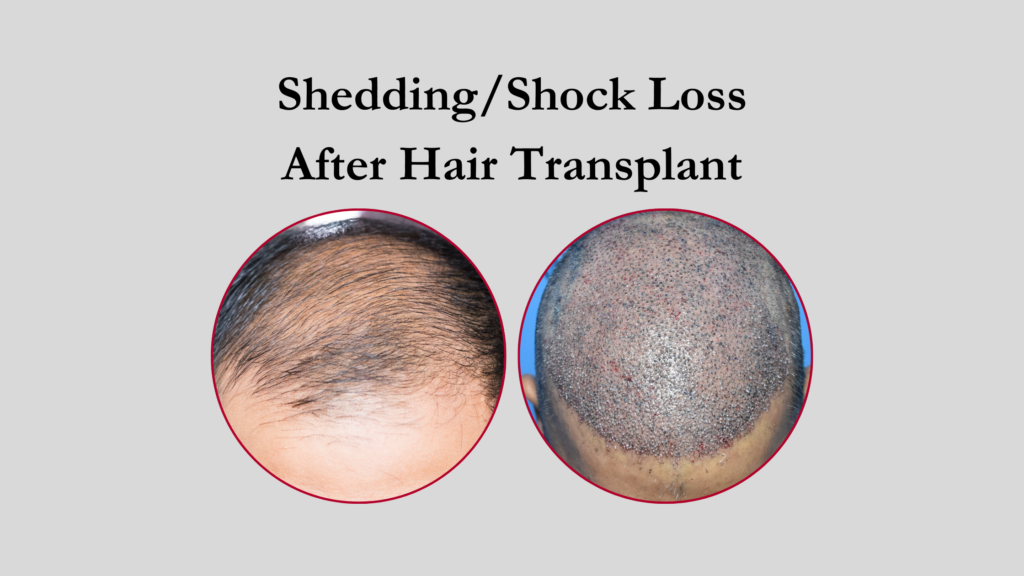
A hair transplant is a life transforming experience for everyone who achieved great results from a good reputable clinic. However, a common concern among patients is shedding after the procedure, often called shock loss. Seeing transplanted hair fall out post your hair transplant surgery makes patients think the procedure is failed! This created stress and anxiety for them. In such situations the patients can rest assured as this is temporary and part of the hair growth process after hair transplant. Lets understand why it happens and how to manage it with the right knowledge to stay confident.
Why Does Shedding Occur After a Hair Transplant?
During a hair transplant, when hair roots are extracted, they go under stress as they remain outside for a while. These hair roots feel insulted due to the change in their normal environment. It also temporarily impacts their natural hair growth cycle. This leads to shedding, but once the roots are implanted to new areas, they remain intact and eventually start producing new stronger hair after the shedding.
Key Causes of Shedding After a Transplant:
- Trauma to Hair Follicles – The extraction and implantation process give mild trauma to the follicles. It temporarily causes transplanted hair to fall out before they enter the new growth phase
- Disruption in Blood Supply – Hair Transplant surgeons use anesthesia and saline during surgery for numbing the area of operation and hydration. This process changes the blood circulation around the transplanted area that temporarily blocks the blood supply to new transplanted hair.
- The Hair Growth Cycle – All hair follows a three-phase growth cycle: anagen (growth), catagen (transition), and telogen (resting). After surgery, the transplanted hairs enter into telogen phase before they resume the normal growth
Most of the patients begin to experience shedding 2-4 weeks after the surgery, which can last up to 3 months
After this phase, they start noticing new and stronger hair growth in about 3-4 months, and the complete result is seen in 12 months.
How to Handle Shedding After a Hair Transplant
While shedding is unavoidable, you can control its impact and promote faster regrowth by taking the following measures:
1. Follow Your Surgeon’s Aftercare Instructions
Proper care after hair transplant is important for a smooth recovery and healing. These include:
- Using a mild, non-medicated shampoo for gentle scalp cleansing
- Avoid using hot water, scratching and rubbing while washing your head. Instead pat and dry your scalp gently
- Never scratch your scalp even if you feel itching on it.
2. Maintain a Healthy Scalp Environment
It is important to create a healthy environment on your scalp for easy and faster hair growth:
- Hydrate and Nourish your scalp by drinking plenty of water.
- You can gently massage your scalp to stimulate blood circulation but try it only after the initial healing period.
3. Consider Medical Treatments
Start taking US FDA-approved medicines like minoxidil, finasteride and nutrition supplements before and after hair transplant as per doctor recommendation. This can make your hair roots healthier so they might not fall out excessively during the shedding phase.
Note: Always consult your doctor before starting any medication.
4. Adopt a Nutrient-Rich Diet
A balanced diet plays a vital role in hair health. Your daily diet should focus on eating foods rich in protein like lean meats, lentils, eggs, beans and dairy products that are good for hair growth. Vitamins like A, C, D, and E, Iron and zinc that will help in new hair formation
5. Be Patient and Trust the Process
Always remember, shedding can be an emotional challenge, but it is a fleeting phase. It is a sign that your hair follicles are adjusting to a new environment and preparing for new growth. The Hair Transplant Results can take time as full density usually appears between 9-12 months after the transplant
When to Seek Medical Advice
While shedding is normal, consult your surgeon if:
- Hair loss persists beyond 8 weeks post-transplant.
- Shedding spreads outside the transplanted area.
You notice redness, excessive itching, or pain, which could indicate infection